+1
+1
+1
+1
+1
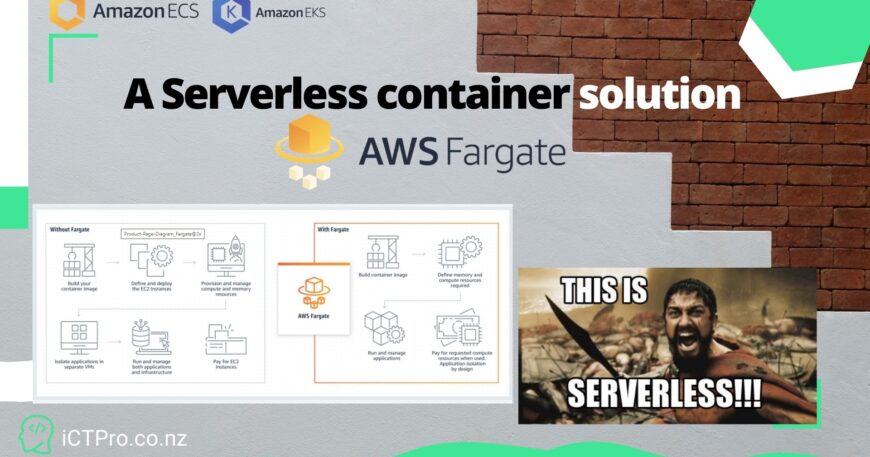
What if I say, you can deploy container images in the serverless environment in AWS without monitoring or Managing. Do not have to worry about nodes or components, just worry about VCPU and Vmemory for the container for one time.
You focus on what you are building and operating apps in Elastic container Services or Kubernetes Services. You won’t have the operational overhead of Scaling, Patching, securing, and Managing servers.
Fargate allows you from .25 to 4 VCPU to your individual container and from .5 to 8 GB of RAM. More flexibility in scaling. Fargate does not have natively build storage( persistence storage). You can attach EFS if you want for your container.
Let’s start with fargate.
We will configure an AWS VPC, create a cluster, create a task definition, create a container image, Deploy container for nginx server – Check out Pricing.
Prerequisite
AWS account
Administrative privileges for the user
A Container image from docker hub or your personal repo
Step 1
Create a VPC
Step 2 – Create a Cluster
Step 3 Create a Task Defenition.
Step 4 Adding a container
Step 5 Deploy a task using task definition.
Step 6 Wait and See the MAGIC.
Share on

